[教程][C#][算法] A* 寻路算法入门——详解 + 实现
06 Nov 2013玩网游的自动寻路是不是很帅?网上有一些破解迷宫的程序,是不是很帅?
给定一个有多个节点的路径的图形,A*算法(读做A星算法)是求从一点到另一点的最低成本的算法(也就是最短的路径,当然这里“最短”是相对的)。
这篇文章非常基本,专门给像我这种刚刚入门的新手。
【区域分割】
假设说我们有一副图:

现在有一个人在绿色的地方
然后红色的地方是墙壁(不能通过)
然后那个人要一最短的时间从绿色的地方 走到 紫色的地方
为了方便,我们把开始的地方(绿色部分)取名为A点
结束(紫色部分)为B点
问题简化为:找出从A点直B点最短的路径。
那要怎么搜索呢?
看过地板上的地砖么?地砖是不是把整个地板分成了一格一格的?
所以我们把我们的地图(就叫做地图吧)分割成一格一格的,像这样:
那样是不是方便多了?
这些一格一格的“地砖”叫做“节点”,分割搜索区域是寻路简单化,而且可以直接将其储存进一个二维数组内。
寻路算法就是找出能从A到B的方格,然后这些方格就组成了我们所需要的“路径”
找出路径之后,那个人就能从A点走到B点了(废话..)
你当然可以把整个地图分成不同的形状:三角形、正方形、矩形等等
但是为了方便起见,在这里我们就用矩形吧!
【开始搜索】
把搜索区域化成一堆节点后,就是开始搜索了!
要如何搜索?
1、从A点开始,把A点加入一个“开放列表”
开放列表中的方格可能会是待会儿会经过的路径,也可能不是
当前的开放列表之中只有A点一个
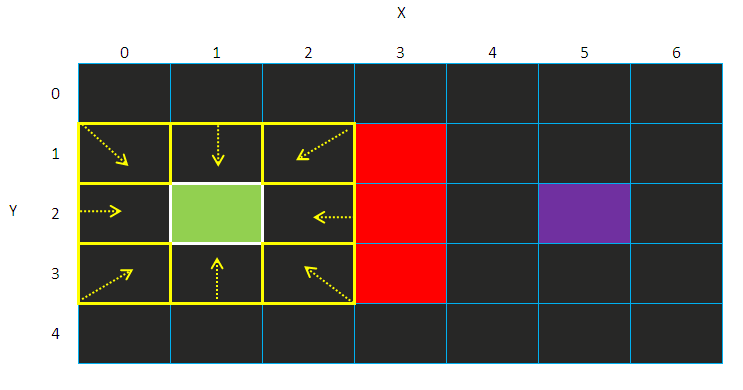
2、检查A点相邻的方格,让后将它们也一起加入开放列表之中(相邻的都要加入,别管那个节点能不能通过)
对于每一个相邻的方格,将A点设为他们的“父亲”,这点很重要
3、从开放列表去掉A,加入“封闭列表”内
最后得到的是这样:
黄色框的是在“开放列表”之中
白色框的是在“封闭列表”之中
4、接下来就是从开放列表之中选一个相邻的方格,然后在重复步骤
那么,要选哪一个方格呢?
选F最小的那个!
【计算F值】
F = G + H
F值决定那个方格会成为路径
这里的:
G = 从A点开始到当前的点所需要的移动开销
H = 从当前方格到目的地方格的估计移动开销。
【计算G值】
G值是从A点开始到当前的点所需要的开销
当前的点就是那些相邻的方格
在这里:
水平/垂直移动的开销 = 10
对角线移动的开销 = 14
怎么算出来的?
很简单,就是一个边长为1的直角三角形呗!
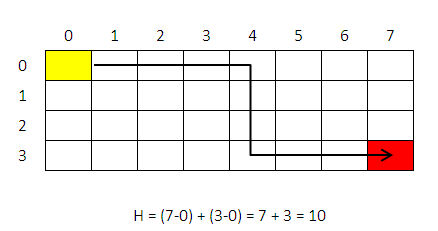
【计算H值】
有很多方法可以估算H值
这里用的叫做 Manhattan 方法,它并不考虑路途中的任何障碍物
H = 当前的点与目的地点的垂直距离 + 当前的点与目的地点的水平距离
像这样:
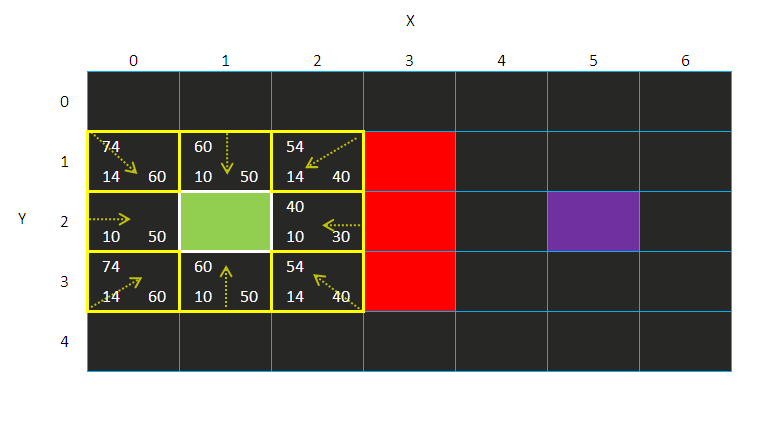
这里左上角是F
左下角是G
右下角是H
【继续搜索】
1、我们从开放列表之中选择拥有最小F值的方格
2、从开放列表之中将其移除,加入到封闭列表之中
3、检测该方格所有的相邻方格,计算F值。
1、忽略那些已经在封闭列表之中的方格
2、如果有相邻方格在开放列表之中,依旧计算其F值,然后与之前计算过的F值比较,如果当前的F值小,覆盖之前计算出来的F值,并将其的父方格设为当前方格
4、将相邻的方格的父方格设置为当前方格
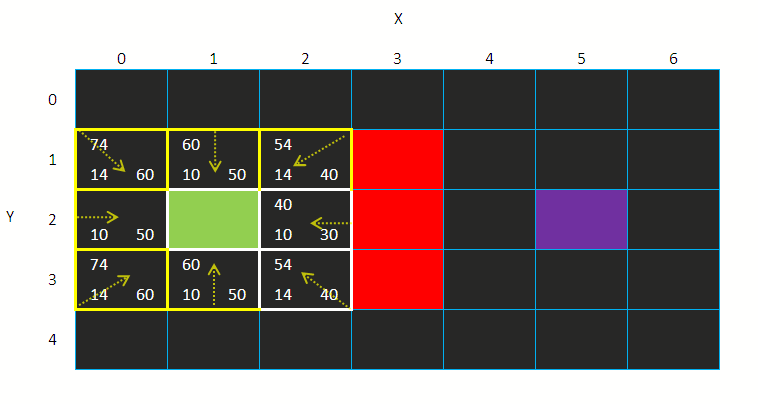
来看看例子
在这里坐标(2,2)的方格拥有最小的F值(40)
所以我们选择它,然后将其放入封闭列表之中
现在它的右边、右上角、右下角是墙,左边的起始方格已经在封闭列表之中了,所以忽略
现在只剩下4个待检测的方格——左上角、左下角、上、下
那些方格都已经在开放列表之中了
所以我们计算然后比较他们的F值
先忽略之前计算过的F值
我们得到的F值是:
(注意G值的变化)
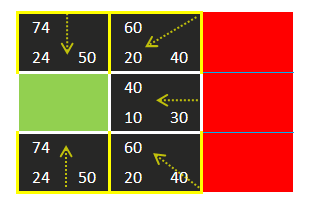
可是他们都比之前算出来的F值大
所以我们都忽略现在计算出来的F值,用回之前计算的F值
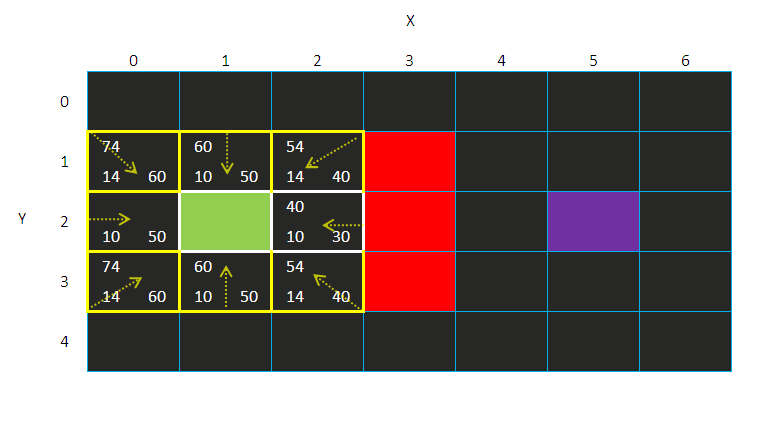
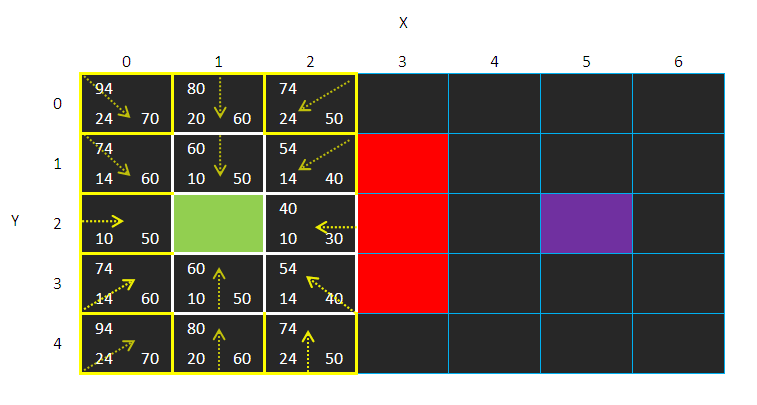
现在我们的开放列表只剩下7个方格了
有最小F值的方格有两个,但是选那个都没有关系
我们就选(2,3)吧!
从开放列表中移除,加入封闭列表之中
然后计算相邻方格的F值
加入开放列表,比较F值,然后设置父方格:

发现到没?
我没有直接检测墙下的方格(3,4)
这事能设定的
如果你不要有人能直角穿过墙角的话,当遇到墙壁时,就不要检测对角的方格
那个方格留给别个方格
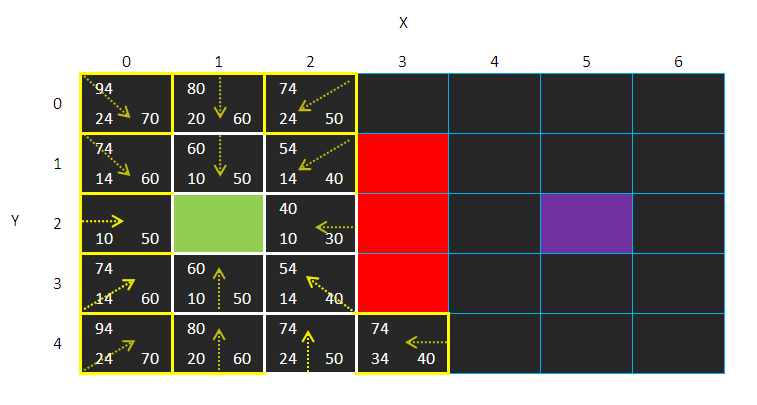
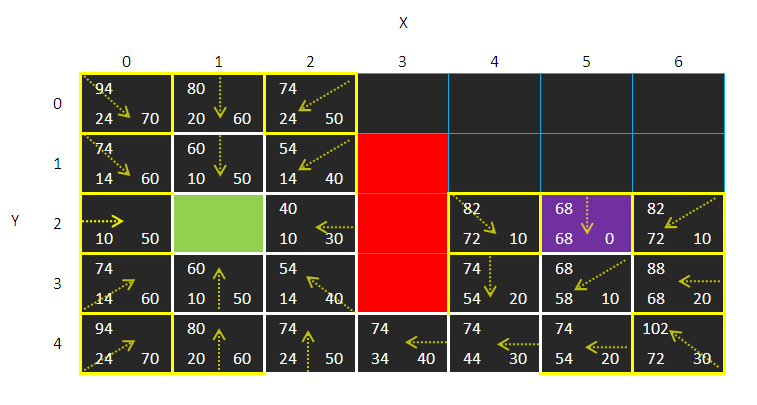
然后搜索继续:

有没有发现到(1,4)的方格的父方格变化了?
本来是(2,3)的

原因是F值更加小了 (之前的 88 和 80)
很明显的路径(1,2)-> (2,3) –> (1,4)比路径(1,2)->
(1,3)->(1,4)更长
我们要最短的路径嘛!
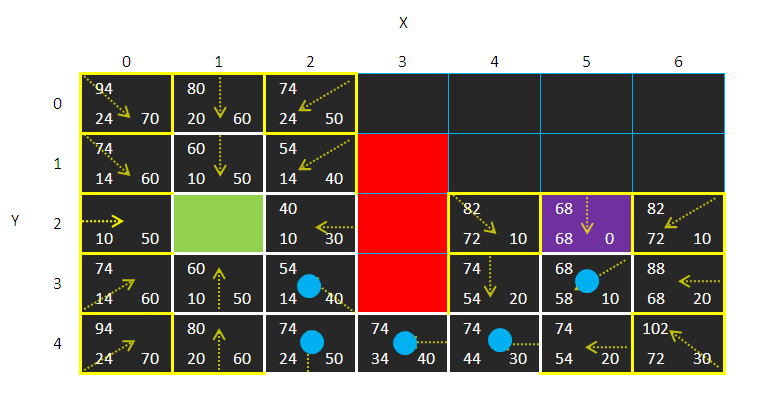
继续搜索:
接下来就不详解了
步骤都一样的
到这里
目的地方格已经有父方格了
如何找出路径呢?
只要中目的地方格沿着走到下一个父方格,一直到起始方格就好了!
先这样:
【C#实现】
整个C#实现A* 寻路算法的代码我推到GitHub 上去了:
https://github.com/garyng/PathFinding
这里的代码仅供参考
不一定是最好、最优的
这个是Node class
代表每一个节点
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.Drawing;
namespace PathFinding
{
public class Node
{
private int _h;
private const int _count = 8; //properties count - for indexing
private Point _pos;
private Node _parent;
private int _g;
private Node _dLeft;
private int _f;
private Node _uLeft;
private Node _dRight;
private Node _uRight;
private Node _down;
private Node _up;
private Node _right;
private Node _left;
private bool _isWall;
public Node()
{
this.Left = null;
this.Right = null;
this.Down = null;
this.Up = null;
this.URight = null;
this.ULeft = null;
this.DLeft = null;
this.DRight = null;
}
public Node(Node left, Node right, Node down, Node up, Node uRight, Node dRight, Node uLeft, Node dLeft)
{
this.Left = left;
this.Right = right;
this.Down = down;
this.Up = up;
this.URight = uRight;
this.ULeft = uLeft;
this.DLeft = dLeft;
this.DRight = dRight;
}
private Node SwitchNodeProp(int index, Node value = null)
{
switch (index)
{
case 0:
//Up
return ReturnNodeProp(ref _up,value);
case 1:
//URight
return ReturnNodeProp(ref _uRight, value);
case 2:
//Right
return ReturnNodeProp(ref _right, value);
case 3:
//DRight
return ReturnNodeProp(ref _dRight, value);
case 4:
//Down
return ReturnNodeProp(ref _down, value);
case 5:
//DLeft
return ReturnNodeProp(ref _dLeft, value);
case 6:
//Left
return ReturnNodeProp(ref _left, value);
case 7:
//ULeft
return ReturnNodeProp(ref _uLeft, value);
}
return null;
}
private Node ReturnNodeProp(ref Node Prop, Node value = null)
{
if (value == null)
{
return Prop;
}
else
{
Prop = value;
return null;
}
}
public Node this[int index]
{
get
{
return SwitchNodeProp(index);
}
set
{
SwitchNodeProp(index, value);
}
}
public int Count
{
get
{
return _count;
}
}
public bool isWall
{
get
{
return _isWall;
}
set
{
_isWall = value;
}
}
public Node Left
{
get
{
return _left;
}
set
{
_left = value;
}
}
public Node Right
{
get
{
return _right;
}
set
{
_right = value;
}
}
public Node Up
{
get
{
return _up;
}
set
{
_up = value;
}
}
public Node Down
{
get
{
return _down;
}
set
{
_down = value;
}
}
public Node URight
{
get
{
return _uRight;
}
set
{
_uRight = value;
}
}
public Node DRight
{
get
{
return _dRight;
}
set
{
_dRight = value;
}
}
public Node ULeft
{
get
{
return _uLeft;
}
set
{
_uLeft = value;
}
}
public Node DLeft
{
get
{
return _dLeft;
}
set
{
_dLeft = value;
}
}
public int F
{
get
{
return _f;
}
set
{
_f = value;
}
}
public int G
{
get
{
return _g;
}
set
{
_g = value;
}
}
public int H
{
get
{
return _h;
}
set
{
_h = value;
}
}
public Node Parent
{
get
{
return _parent;
}
set
{
_parent = value;
}
}
public Point Pos
{
get
{
return _pos;
}
set
{
_pos = value;
}
}
}
}每一个节点的相邻方格储存在相应的属性内
并且可以直接以index 来获取:
这个是初始化一个二维Node 数组的代码:
private void InitNodes(ref List<List<Node>> nodes)
{
for (int x = 0; x < _width; x++)
{
List<Node> nX = new List<Node>();
for (int y = 0; y < _height; y++)
{
Node nY = new Node();
nY.Pos = new Point(x, y);
//nY.F = x * 100 + y;
//Up
if (y > 0)
{
nY.Up = nX[y - 1];
nX[y - 1].Down = nY;
}
//Left
if (x > 0)
{
nY.Left = nodes[x - 1][y];
nodes[x - 1][y].Right = nY;
}
//UpLeft
if (x > 0 && y > 0)
{
nY.ULeft = nodes[x - 1][y - 1];
nodes[x - 1][y - 1].DRight = nY;
}
//DownLeft
if (x > 0 && y < (_height - 1))
{
nY.DLeft = nodes[x - 1][y + 1];
nodes[x - 1][y + 1].URight = nY;
}
nX.Add(nY);
}
nodes.Add(nX);
}
}这个是核心寻路算法:
private void FindPath(ref List<List<Node>> nodes, Node start, Node end)
{
List<Node> open = new List<Node>();
List<Node> close = new List<Node>();
open.Add(start);
while (open.Count > 0)
{
close.Add(open[0]);
Node pendingNode = open[0];
open.RemoveAt(0);
for (int i = 0; i < pendingNode.Count; i++)
{
Node current = pendingNode[i];
if (current == null || current.Equals(start) || current.isWall)
{
continue;
}
int h;
int g;
int f;
if (i % 2 == 0)
{
//Up Right Down Left
g = pendingNode.G + 10;
}
else
{
// URight DRight DLeft ULeft
//check for walls
//|X
//|_
if (pendingNode[(i + 1) % 8].isWall || pendingNode[i - 1].isWall)
{
continue;
}
g = pendingNode.G + 14;
}
h = (Math.Abs(end.Pos.X - current.Pos.X) + Math.Abs(end.Pos.Y - current.Pos.Y)) * 10;
f = h + g;
if (f < current.F || current.F == 0)
{
current.G = g;
current.H = h;
current.F = f;
current.Parent = pendingNode;
open.Add(current);
}
if (current.Equals(end))
{
List<Node> paths = new List<Node>();
Node path = end;
while (path.Parent != null)
{
paths.Add(path);
path = path.Parent;
}
open.Clear();
VisualizePath(paths);
break;
}
}
open = open.OrderBy(item => item.F).ToList();
}
}注:这里没有实现“忽略已经在封闭列表中的节点”
【截图】
无图无真相,所以就发图:
红色的是墙壁
白色的是起始点
蓝色的是终点
Published by Gary Ng